From sensors to batteries: Two decades of graphene, how safe is it?
Rapid development in many fields
Graphene was first isolated in 2004. It has the characteristics of ultra-thin, ultra-strong, ultra-flexible, and is known as a "miracle" material. It may be used in electronic products, mobile phone screens, clothing, paint, water purification, and other fields. Recently, engineers at the University of California, San Diego, developed an ultra-sensitive sensor made of graphene that can detect extremely low concentrations of lead ions in water... The device can detect lead down to femtomolar levels and is 1 million times more sensitive than previous sensing technologies.
Studies have shown that lead concentrations in drinking water reaching several parts per million may cause harmful consequences, such as hindering human growth and development. The new detection device consists of a single layer of graphene mounted on a silicon wafer. Graphene has excellent electrical conductivity and surface area-to-volume ratio, providing an ideal platform for sensing applications. The researchers enhanced graphene's sensing capabilities by attaching a linker molecule to its surface. This linker acts as an anchor for ion receptors and, ultimately, for lead ions.

The researchers used short single-stranded DNA or RNA aptamers as ion receptors. These receptor molecules are selective for specific ions. The researchers further enhanced the receptor's affinity for lead ions by adjusting the receptor's DNA or RNA sequence. This ensured the sensor would only be triggered when bound to lead ions.
The researchers analyzed the system's thermodynamic parameters, such as binding energy, capacitance changes, and molecular conformation, and found they played a key role in optimizing sensor performance. By optimizing these thermodynamic parameters and the design of the entire system, the researchers created a sensor that can detect lead ions with unprecedented sensitivity and specificity, achieving detection limits at the femtomolar level. Although this technology is still in the proof-of-concept stage, the researchers hope to use it for actual detection, with the ultimate goal of "detecting even a single lead ion in water."
Graphene battery has more advantages than traditional batteries
Graphene is a single-layer honeycomb two-dimensional lattice material composed of carbon atoms. Its thickness is only one atomic layer, but its strength is 200 times higher than steel. Graphene has excellent thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, and optical properties and is known as the "King of New Materials." The discovery of graphene has brought revolutionary changes to the energy field, such as solar cells, supercapacitors, hydrogen storage, etc.
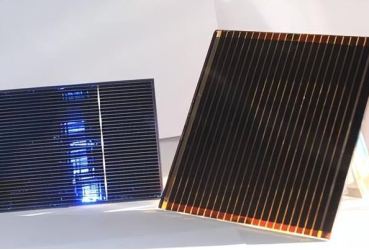
As a new material, graphene batteries have certain advantages
1. The charging speed is relatively fast. The charging speed of graphene batteries is much faster than lead-acid batteries. Graphene batteries can be charged 80% in one hour using a fast charge charger for batteries of the same specifications. In contrast, ordinary lead-acid batteries may take six to eight hours to charge fully, so it is necessary to Much slower.
2. The future development prospects are good. Because graphene batteries have strong conductivity, are relatively light, small in size, and have relatively high strength, the industry widely favors graphene batteries. They are believed to be able to replace lithium batteries in the future.
Battery mass production is still a problem
It will take time to achieve the goal
Regarding the mass production of graphene batteries, short-term predictions and longer-term prospects exist. The field of graphene batteries is still in its early stages of development. However, many technology companies and research institutions are researching and developing graphene batteries, and mass production still needs to improve.
First, the production cost of graphene batteries is relatively high, and there needs to be a mature commercial production technology. Secondly, the safety issues of graphene batteries during the production process also deserve attention. Graphene itself is relatively easy to burn. Therefore, in the production process of graphene batteries, how to ensure the safety of the production process is an issue that needs to be solved urgently. In addition, like many new materials, the quality and quality control of graphene are also issues that must be addressed during the production process. This is the main problem restricting the mass production of graphene batteries.

However, although many problems still restrict the mass production of graphene batteries, the application prospects of graphene batteries are worth looking forward to. On the one hand, graphene batteries have many unique properties compared to traditional batteries. First, graphene batteries have a high charge storage capacity. Because graphene has extremely high electrical conductivity and conductivity, graphene batteries can store a greater amount of charge than other batteries. At the same time, the cycle life of graphene batteries is also longer and can better meet reusability needs.
Not only that, but graphene batteries also have excellent fast charge and discharge performance and high power output capabilities, allowing them to perform better at high speeds and in various application scenarios. On the other hand, the development and application of graphene materials are rapidly developing. Its applications in energy storage, batteries, solar cells, and semiconductor industries have been extensively explored and researched. As graphene technology becomes increasingly mature, graphene batteries are expected to be further promoted and applied. Therefore, although graphene batteries face difficulties in mass production, their application prospects are still broad. In the future, with the development of graphene technology and the decline of production costs, graphene batteries will surely be promoted and applied, bringing more reliable, efficient, and sustainable energy solutions.
First clinical trial
Graphene nanomaterials are safe.
British researchers have announced an important finding: The first strictly controlled exposure clinical trial in humans shows that inhaling certain types of graphene has no short-term adverse effects on lung or cardiovascular function. This means that graphene, a nanomaterial, can be developed safely without posing significant risks to human health. In addition, scientists are actively exploring graphene's role in targeted treatments for cancer and other diseases, such as making it into implantable devices and sensors. However, before medical applications, all nanomaterials must be tested for potential adverse effects.

The human trials used ultrapure graphene oxide nanoflakes, a miscible material with water. Researchers from the University of Edinburgh recruited 14 volunteers who participated under strictly controlled exposure and clinical monitoring conditions. Volunteers wore masks and breathed ultrapure graphene oxide for 2 hours while cycling in a specially designed mobile laboratory. Their lung function, blood pressure, coagulation, and blood levels were measured before and every two hours after exposure. Inflammation levels. A few weeks later, the volunteers returned to the clinic for repeated controlled exposures to different qualities of graphene oxide or clean air for comparison.
The results showed that inhaling ultrapure graphene oxide had no adverse effects on lung function, blood pressure, or other biological parameters. The researchers noted slight indications that inhaling the substance might affect the way blood clots, but the effects were very small. However, further investigation is needed to determine the potential effects of higher doses and prolonged exposure to graphene.
Researchers say nanomaterials such as graphene are promising, but they must be manufactured safely before they can be used more widely in life. A giant step forward in understanding how graphene affects the human body has been taken by exploring the safety of this unique material in human volunteers. The discovery could open the door to developing new devices, treatments, and monitoring techniques.
Graphene Supplier
Graphite-crop corporate HQ, founded on October 17, 2008, is a high-tech enterprise committed to the research and development, production, processing, sales and technical services of lithium ion battery anode materials. After more than 10 years of development, the company has gradually developed into a diversified product structure with natural graphite, artificial graphite, composite graphite, intermediate phase and other negative materials (silicon carbon materials, etc.). The products are widely used in high-end lithium ion digital, power and energy storage batteries.If you are looking for graphite powder for battery li-ion anode, click on the needed products and send us an inquiry: sales@graphite-corp.com







