Negative electrode materials for lithium batteries
The common active materials for negative electrodes are mainly divided into five types:
1.Carbon negative electrode materials: Currently, most of the negative electrode materials used in lithium-ion batteries are carbon materials, including artificial graphite, natural graphite, mesophase carbon microspheres, petroleum coke, carbon fiber, pyrolysis resin carbon, etc.

2. Tin based negative electrode materials: Tin based electrode materials can be separated into tin oxide and tin based composite oxide
3. Lithium containing transition metal nitride negative electrode materials
4. Alloy negative electrode materials: Including silicon based alloys, germanium based alloys, aluminum based alloys, antimony based alloys, magnesium based alloys, and other alloys
5. Nano oxide materials and carbon nanotubes
At present, the negative electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries are mainly divided into two categories: carbon materials and noncarbon materials. Compared with other lithium embedded negative electrode materials, carbon materials have advantages such as high specific capacity, low electrochemical potential, good cycling performance, low cost, non-toxic, and stability in air, making them the most mature negative electrode material for lithium-ion batteries in the current market.
Most noncarbon negative electrode materials are currently in the research and development stage: noncarbon negative electrodes mainly include transition metal oxides, multi-element lithium alloys, lithium metal nitrides and transition metal nitrides, phosphides, sulfides, silicides, and so on. Although these materials have more significant advantages over carbon materials in certain aspects, such as higher specific capacity, better cycling performance, and better rate performance, there are still many problems to be solved, such as volume expansion, voltage hysteresis, and poor safety during charging and discharging processes. At present, the most likely breakthrough is silicon materials, which have been applied in the market, but their cost and price are high, and their performance needs further verification and evaluation. They have yet to be widely deployed.

Energy Cube: Lithium Electronic Battery
Lithium-ion batteries are a type of secondary battery (rechargeable battery) that mainly relies on the activity of lithium ions in between the positive and unfavorable electrodes for operation. Throughout the charging and discharging procedure, Li+is intercalated and disembedded backward and forward between both electrodes: throughout charging, Li+is disembedded from the positive electrode, embedded right into the negative electrode via the electrolyte, and the negative electrode remains in a lithium-rich state. When discharging, the reverse is true.
Lithium batteries are split into lithium batteries and lithium-ion batteries. Both mobile phones and laptop computers make use of lithium-ion batteries, commonly called lithium batteries. Batteries generally make use of products, including lithium as electrodes, which are depictive of modern-day high-performance batteries. Nevertheless, actual lithium batteries are rarely used in daily electronic products because of their high threat.
Lithium-ion batteries were first efficiently created by Sony Corporation of Japan in 1990. It involves installing lithium ions into carbon (petroleum coke and graphite) to develop a negative electrode (traditional lithium batteries make use of lithium or lithium alloys as the adverse electrode). LixCoO2 is frequently utilized as the favorable electrode material, along with LixNiO2 and LixMnO4. The electrolyte uses LiPF6+ethylene carbonate (EC)+dimethyl carbonate (DMC).
Petroleum coke and graphite as adverse electrode materials are safe and have sufficient resources. Lithium ions are installed in carbon, conquering the high activity of lithium and solving the safety and security issues of standard lithium batteries. The favorable electrode LixCoO2 can achieve high levels of charging and releasing efficiency and lifespan, lowering expenses. Simply, put the detailed efficiency of lithium-ion batteries has actually been boosted. It is anticipated that lithium-ion batteries will occupy a large market in the 21st century.

What are the positive and negative electrodes (anode and cathode) of a lithium battery
An electrochemical battery is consisted by a cathode, an anode, and an electrolyte that acts as a catalyst. During charging, positive ions will form at the cathode/electrolyte interface. This causes electrons to move towards the cathode, generating potential between the cathode and anode. Release is achieved by causing current to flow back from the positive pole through an external load to the negative pole; when charging, the current flows in another direction.
The battery has two separate paths; One is the circuit through which electrons flow to supply power to the load, and the other is the path through which ions move between electrodes through separators that act as electronic insulators. Ions are atoms that lose or acquire electrons and are charged. The diaphragm electrically isolates the electrodes but allows for ion movement.
Anode and cathode
The battery electrode that releases electrons during the discharge process is called the anode; The electrode that absorbs electrons is the cathode.
The battery's anode is generally the negative electrode, and the cathode is commonly the positive electrode. This seems to violate convention, as the anode is the terminal through which current flows. Follow this sequence for vacuum tubes, diodes, or rechargeable batteries. However, removing electricity from the battery during discharge can cause negative polarization of the anode. Because of the fact that batteries are energy storage devices that provide energy, the anode of the battery is always the negative electrode.
The anode of lithium ions is carbon, but the order of lithium metal batteries is opposite. The cathode here is carbon, and the metal lithium is the anode. With almost no exceptions, lithium metal batteries are not rechargeable.

The relationship between charging and discharging, anode and cathode electrodes, and negative and positive electrodes of lithium batteries
From the most fundamental definition, it is the anode that undergoes the oxidation reaction and the cathode that undergoes the reduction reaction. The positive electrode has a high potential, while the negative electrode has a low potential. The positive and negative poles are fixed and unchanging, and different charging and discharging processes can cause changes in the negative and positive poles. Generally, primary batteries refer to positive and negative electrodes, while electrolytic cells refer to cathode and anode electrodes, so it is better for batteries to remember positive and negative electrodes.
Anode: Electrons are lost and oxidized.
Cathode: The electrons are reduced.
Positive: The side with high potential.
Negative: The side with low potential.
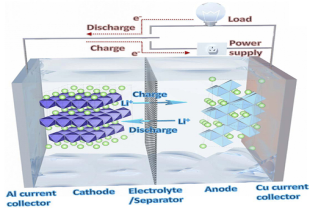
Throughout charging
Lithium ions are removed from the latticework of the anode electrode material and are placed into the lattice of the cathode electrode material after traveling through the electrolyte, resulting in lithium enrichment in the negative electrode and lithium deficiency in the positive electrode;
The charging procedure can be treated as an electrolytic cell: the anode pole equals the positive pole.
Electrolysis is an easy process that takes in energy and reacts vice versa with the critical battery. The anode loses electrons and undergoes an oxidation response, while the cathode gains electrons and undergoes a decrease response.
Throughout discharge
Lithium ions are removed from the latticework of the negative electrode product. They are placed into the latticework of the positive electrode product after traveling through the electrolyte, resulting in abundant lithium in the positive electrode and inadequate lithium in the negative electrode.
The discharge procedure can be dealt with as a key battery: The positive electrode is equal to the cathode electrode.
A main battery is a spontaneous procedure that releases power, gains electrons from the positive electrode, undergoes a decreased response, sheds electrons from the negative electrode, and goes through an oxidation response. The electrons relocate from the negative electrode to the positive electrode, and the current circulations from the positive electrode to the negative electrode.

Supplier
Graphite-crop corporate HQ is a high tech enterprise committed to the research and development, production, processing, sales and technical services of Silicon materials, we are high quality silicon supplier. Our Company has a diversified product structure with silicon carbon materials, and other negative materials (graphite materials, etc.). Please feel free to contact us. Or click on the needed products and send us an inquiry: sales@graphite-corp.com







